The TIMES_Heat Model
In the RewardHeat project, the well-established TIMES (The Integrated MARKAL-EFOM System) energy system model generator is used for the analysis (ETSAP, M. Gargiulo, 2009). For the study, a heating sector model (TIMES_Heat) was developed and applied for each demonstrator. The TIMES_Heat model represents the heating sectors in the studied countries, including the heat generation in district heating systems and individual heating units in buildings. The electricity system as well as international markets for fuels are treated exogenously. Energy efficiency measures and heat demand projections are provided as exogenous inputs to the model.
The TIMES_Heat model minimizes the cost of satisfying the heating demand for each country, considering the constraints that are defined in the model, for example, emissions, resource availability, etc.
The start year of the model is 2015. In that year, the heating sector is represented with exisiting fuel mix and heat generation units. The existing technologies are phased out gradually and are replaced with the new technologies, considering their costs, efficiencies, availabilities, lifetimes, etc.
- Start year of the model: 2015
- Time horizon: 2015-2052
- Time resolution: Eight time slices per year (four seasons, day and night)
Schematic representation of heat sector in TIMES_Heat model
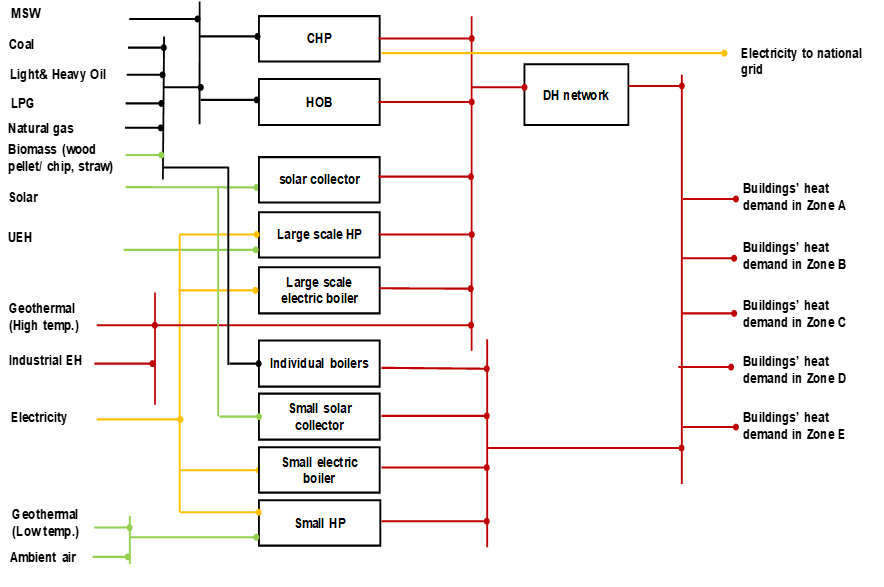
Figure 1. Simplified representation of the heating sector in the TIMES_Heat model (TIMES-Heat model, Sandvall, 2020)
Air pollutants
Three air pollutants i) Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), ii) Sulfur Oxides (SOx) iii) particles less than 2.5 μm (PM2.5) were estimated for all heat production technologies that are supplying the heat demand for each scenario. The methodology used here is multiplication of heat output from the respective technologies (PJ) and emissions factor per each substance, technology and fuel (kt/PJ).
For air pollutant calculations, the TIMES model is soft-linked with the GAINS model (IIASA, 2018). Heat output is retrieved from the TIMES_Heat model and linked with the unique emission factor for respective technology defined in the GAINS model.
For detailed explanation please refer to the respective report 1 section 17.11.
For more information:
1 Link to the report where detailed information about the TIMES_Heat model and for each country that is modeled: https://www.rewardheat.eu/Download?id=file:83807000&s=-333193579074902488
2 Short description of the TIMES modeling framework: https://iea-etsap.org/index.php/etsap-tools/model-generators/times
3 Link to the TIMES model documentation, which contains information about the modeling framework and how to use the tool: https://iea-etsap.org/index.php/documentation